
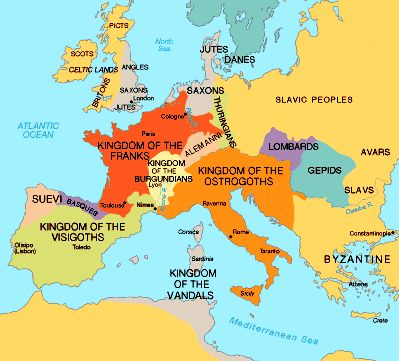
France was one of the first nation-states. Nationalism often causes groups to want their own countries, so it contributed to the rise of modern nation-states. Nationalism is the belief that people should be loyal to their nation, the people with whom they share land, culture, and history. Over time, strong kings gained power over feudal lords, and nationalism evolved. They gave some land to nobles in exchange for military service by those nobles. This was a political system in which powerful lords owned most of the land. NATIONALISMĭuring the centuries after Rome fell, feudalism gradually developed in Europe. During this time, Europeans gradually developed the nation-state, an independent nation of people with a common culture. The period between the fall of Rome and the Renaissance is called the Middle Ages.
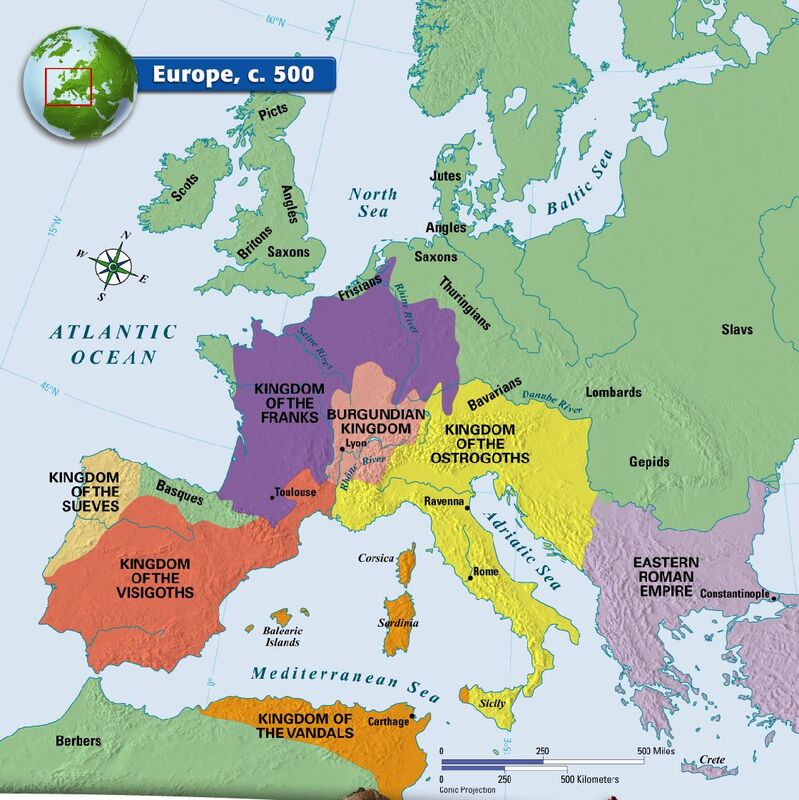
In Germany, Protestants live mainly in the north and Catholics in the south of the country. The Netherlands, Switzerland, and Germany contain both Protestants and Catholics. Mutual hostility led Catholics and Protestants to fight religious wars that tore Europe apart. That began the Reformation, a period when many Christians broke away from the Catholic Church and started Protestant churches. In 1517, Martin Luther published 95 statements that criticized church practices that he believed were wrong. Some people even began to question the Catholic Church. During the Renaissance, scholars questioned authority. Western Europe remained a region of small, competing kingdoms.Ī religious movement created new differences. However, his empire began to fall apart soon after his death. In the late 700s, a Germanic king, Charlemagne, conquered most of the region. Germanic languages are still spoken there. But Rome never fully conquered the Germanic tribes that migrated into the lands east of France. French is one of the Romance languages that evolved from Latin (Rome's language). By 50 B.C., the Roman Empire had conquered the Celtic tribes in what is now France. One cultural division, language, dates from ancient times.

Western Europe's cultural divisions have historic roots. Switzerland and the Benelux countries of Belgium, the Netherlands, and Luxembourg have their own cultures-but also have been influenced by Germany and France. They are the two largest countries, and their access to resources, ports, and trade routes helped them to build productive economies.įrench culture is strong in France and Monaco German culture is strong in Germany, Austria, and Liechtenstein. A History of Cultural Divisionsįrance and Germany are the dominant countries in Western Europe. France and Germany have long had a deep rivalry, based in part on cultural differences. Why? Perhaps it was because he had a German last name and came from Lorraine, a region that had switched between French and German rule many times. During World War I, some French patriots considered him a disloyal foreigner. A HUMAN PERSPECTIVE Today, the French call Emile Durkheim the father of French sociology (the study of society).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
